FTE Meaning: Understanding Full-Time Equivalent
Full-time jobs often have a standard number of hours per week. Many companies use 40 hours as full-time. Others may use 35 or even 30 hours as the benchmark for full-time.
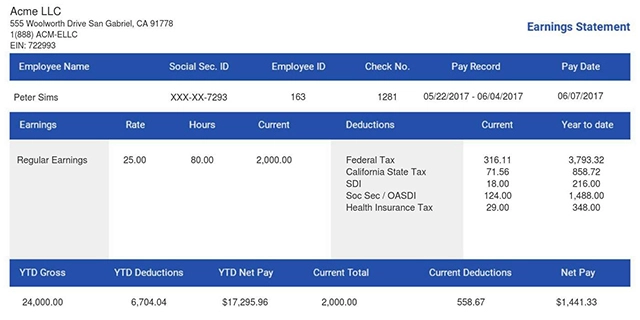
In fact, the U.S. Department of Labor has no fixed definition of full-time under the law. It is up to each employer to decide what their company arrangement would be for full-time employees. Here is where FTE meaning becomes very critical. A paystub template lays out regular hours, overtime, and pay in a consistent format.
FTE helps workers and managers agree on a full-time schedule. In this article, we will delve into the FTE meaning in business and how it affects your pay.
- What Does Full-Time Equivalent Mean?
- FTE Meaning in Business: How Does It Work?
- How Companies Use FTE for Budgeting and Payroll
- Understanding Pay and Benefits by Hours Worked
- FTE Meaning Job Hours: How To Calculate Full-Time Equivalent
- Comparison Table for FTE in Business
- Why FTE Is Important for Planning and Compliance
- Final Thoughts
What Does Full-Time Equivalent Mean?
FTE meaning "full-time equivalent," is a way to count and compare work hours. Instead of counting people, FTE counts how many full-time workers those hours equal. For example, one person working 40 hours a week is 1.0 FTE for one full-time worker.
Two people working 20 hours each also equal 1.0 FTE. The FTE meaning in business, schools, and government agencies helps to compare jobs and workload easily. It shows up in many contexts. Some employers create paystubs records that link scheduled hours and FTE status to gross pay.
HR managers use FTE to report how many workers a department has. Small businesses say things like “we have 10 FTE staff.” Even in job ads, you’ll see fractions like 0.8 FTE or 1.0 FTE.
A listing might say 0.8 FTE meaning 80% of full-time. This is used to describe, calculate, and compare total work hours for a business.
FTE Meaning in Business: How Does It Work?
Imagine a person working at an office desk. FTE expresses the percentage of full-time work. If a job is 1.0 FTE, then it is full-time hours.
Some organizations consider 40 hours a week as 1.0 FTE. Half of that, which is about 20 hours, is a 0.5 FTE job. 10% of a full-time, which is about 4 hours a week, is a 0.1 FTE job.
Other organizations and companies may describe full-time differently in formal regulations. For example, healthcare regulations require a minimum of 30 hours a week as full-time. Yet, 40 hours a week is typical for most jobs.
FTE meaning is simply a way to state "this work takes X% of the time of a full-time employee." It tells employees whether they will work part-time or full-time. For example, an FTE of 0.8 is working 80% full-time. That would be 32 hours if 40 is full-time in that company or organization.
That tells you and the employer about pay and benefits. Knowing your FTE meaning helps with work planning. It affects pay, benefits and workload.
Workers can compare jobs with FTE to find the best fit for them. Employers can also use FTE meaning business to schedule work and staff, especially for part-time and full-time employees.
How Companies Use FTE for Budgeting and Payroll
Firms apply FTE to measure their employees and payroll. FTE converts the hours of every employee into full-time worker equivalents. It makes planning easier when accounting for staff in an organization.
Two half-time employees (0.5 FTE) are the same as 1.0 FTE. This alerts a manager that they have a single full-time equivalent employee. Firms track FTE for an array of various reasons:
-
Workforce Planning: Help to calculate how many employees are needed. It shows full staffing as full-time units.
-
Budgeting: Make payroll and cost estimations clear. For example, budgeting for $50,000 to 1.0 FTE means including $5,000 for each 0.1 FTE.
-
Scheduling: Allows shifts and project planning. For instance, if you require a 100-hour project, you can figure out how much FTE (e.g, 2.5 FTE) you need.
-
Compliance: Some regulations incorporate FTE in the rule of count. The Affordable Care Act uses FTE to determine whether an organization must offer health coverage.
-
Reporting: Investors, lenders or agencies may need FTE as a measure of company size. It makes the comparison of companies standard.
When an organization applies FTE, it is then able to include part-time and temporary workers within its total. For example, a small business employs 3 full-time workers and 4 part-timers, each working 10 hours per week.
The part-timers would represent 40 hours (4 × 10), giving a total of 1.0 FTE. The company therefore has 4.0 FTE in total. This assists managers in visualizing the staffing scenario rather than simply head-counting.
Understanding Pay and Benefits by Hours Worked
An FTE salary indicates how salaries scale with hours. If a full-time salary is $50,000 a year, that is 1.0 FTE. A 0.5 FTE would earn around half that ($25,000) if hourly pay is the same. In general, the pay of a part-time worker is proportional to the FTE fraction.
For instance, if a full-time (1.0 FTE) job pays $50,000, then:
-
0.5 FTE (half-time) earns approximately $25,000 (50% of $50,000).
-
0.2 FTE (20% time) earns around $10,000 (20% of $50,000).
When using an hourly rate, multiply hours times rate. This could be full-time salary × FTE fraction = Part-time salary.
This way, $25/hour for 40 hours/week (1.0 FTE) equals $52,000/year. If half-time (0.5 FTE, or 20 hours/week), that is roughly $26,000/year.
Many employers also prorate benefits on FTE. An employee who works full-time might get 2 weeks' vacation, while a 0.5 FTE would get about 1 week.
FTE Meaning Job Hours: How To Calculate Full-Time Equivalent
To calculate FTE, add up the total hours worked and compare the result to a full-time schedule. Here is how to get this done:
-
Choose full-time hours: Identify the hours that are full-time (typically 40 hours/week or 2080 hours/year).
-
Collect hours worked: Add up all the hours of all staff within that time period (week, month, or year).
-
Total hours divided: Divide the sum by your full-time hours.
The result is the Full-Time Equivalent. The number you get is the total FTE. Round or leave as a decimal as needed.
For example:
Three employees might work a total of 120 hours in a week. If the full-time week is 40 hours, then FTE = 120/40 = 3.
Comparison Table for FTE in Business
Here is a comparison table showing FTE values from 0.1 to 1.0, with corresponding weekly hours. It also shows the effect on pay, assuming full-time is $50,000 per year. This table assumes a 40-hour week is 100% (1.0 FTE).
| FTE | Hours per week | Percentage of Full-Time | Annual Pay |
| 0.1 | ~4 hours | 10% | $5,000 |
| 0.2 | ~8 hours | 20% | $10,000 |
| 0.3 | ~12 hours | 30% | $15,000 |
| 0.4 | ~16 hours | 40% | $20,000 |
| 0.5 | ~20 hours | 50% | $25,000 |
| 0.6 | ~24 hours | 60% | $30,000 |
| 0.7 | ~28 hours | 70% | $35,000 |
| 0.8 | ~32 hours | 80% | $40,000 |
| 0.9 | ~36 hours | 90% | $45,000 |
| 1.0 | 40 hours | 100% | $50,000 |
If your workplace uses a different standard (like 35 hours), adjust the hours column accordingly.
Why FTE Is Important for Planning and Compliance
FTE meaning is useful in business and law in a number of ways. Through FTE, the staff can be easily quantified. The most important among them:
-
Business planning
-
Budgeting
-
Scheduling
-
Legal Compliance
-
Equity
-
Economic Reporting
-
Resource Management
For example, a company can state, “We have 120 FTEs”. It will be able to employ 150 payroll personnel and might employ a few part-time employees. This will ascertain their working ability adequately.
Final Thoughts
Full-time equivalent is an easy method of measuring the number of hours worked and is shortened as FTE. An FTE models the working time of one full-time employee. It is applied in law and business as it helps to plan resources, budget and comply.
Understanding of FTE informs employees of their fraction of work and allows the employer to get control over resources. To help you eliminate misunderstandings concerning the hours and salary, you can try out our check stubs maker. We provide easily navigated tools and professional pay stubs. Visit us today!