Semi-Monthly Meaning: Definition, Pay Schedule & Examples
This payroll term refers to a schedule in which workers receive two paychecks each month. The semi-monthly meaning is often confused with biweekly in the United States, yet these are very different schedules.
If you've asked yourself, "What does semi monthly mean?" while reviewing a job offer, you're far from alone. Many workers ask, "What is semi monthly meaning?" when they see it on an offer letter. The difference directly affects your paycheck size, pay dates, and financial planning.
This guide breaks down "What is semi monthly pay?", how it compares to biweekly, and how to calculate your earnings using a pay stub generator.
Key Takeaways
-
Semi-monthly means getting paid twice a month on fixed dates (usually the 1st and 15th), resulting in 24 paychecks per year
-
Biweekly means every two weeks on the same weekday, resulting in 26 paychecks per year
-
On a $50,000 salary, semi-monthly pay is $2,083.33 per check vs $1,923.08 for biweekly
-
Your annual tax burden remains constant regardless of your pay schedule
-
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 19.8% of U.S. businesses use semi-monthly pay
- Key Takeaways
- What Does Semi-Monthly Mean? The Definition Explained
- Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly: Key Differences
- The Semi-Monthly Meaning vs Bi-Monthly and Bi-Weekly
- How To Calculate Semi-Monthly Pay
- Pros and Cons of Semi-Monthly Pay
- Does the Semi-Monthly Meaning Affect Your Taxes?
- How To Choose the Right Pay Schedule
- How the Semi-Monthly Meaning Shows up on Your Pay Stub
- You Might Also Like
- To Sum It Up
What Does Semi-Monthly Mean? The Definition Explained
This payroll frequency is used by about 19.8% of U.S. businesses. Semi-monthly means getting paid in two installments each month on specific, fixed dates. Common pay dates are the 1st and 15th or the 15th and last day of the month. This schedule results in 24 paychecks per year. Unlike biweekly pay, which follows a weekday cycle, semi-monthly pay dates are tied to calendar dates.
So, what does semi-monthly pay mean in practice? If you're a salaried employee, your annual salary gets divided by 24. Each paycheck covers roughly half a month of work. The pay dates don't change, which helps with budgeting for rent and other monthly bills. Most employers process semi-monthly payroll through direct deposit, so funds arrive on the same dates each month.
One common question is "Is semi-monthly twice a month? Yes. It refers to receiving two paychecks each month. The semi-monthly meaning stays the same across all industries and job types.
What does semimonthly mean for hourly workers? The same schedule applies, but your paycheck amount depends on work hours logged. So, what is semimonthly in payroll? It's a set schedule that splits the year into 24 equal payment periods.
Semi-Monthly vs Bi-Weekly: Key Differences
The main difference between semi-monthly and biweekly pay is frequency. When comparing semi-monthly vs bi-weekly schedules, semi-monthly pay gives you 24 paychecks per year on fixed dates. Biweekly pay gives you 26 paychecks on the same weekday every two weeks. On a $50,000 salary, that means $2,083.33 vs $1,923.08 per check.
This table shows the difference between biweekly and semimonthly schedules:
| Feature | Semi Monthly | Biweekly |
| Paychecks per year | 24 | 26 |
| Pay dates | Fixed (1st & 15th) | Same weekday every 2 weeks |
| Paycheck size ($50K salary) | $2,083.33 | $1,923.08 |
| Extra paycheck months | None | 2 months per year |
| U.S. adoption rate | 19.8% | 43% |
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, biweekly is the most common pay schedule in the U.S., used by 43% of businesses.
Is semi-monthly the same as bi-weekly? No. These two pay schedules differ in paycheck amounts and pay dates. The bi-weekly vs semi-monthly debate comes down to structure: calendar dates vs weekday cycles. They are usually about timing, not total pay.
The Semi-Monthly Meaning vs Bi-Monthly and Bi-Weekly
In payroll, bi-monthly means the same as semi-monthly. Workers are paid twice per month, for a total of 24 paychecks per year. So, "What is bi-monthly pay? It's just another way of saying semi-monthly. Bi-weekly means every two weeks for 26 paychecks a year. The mix-up comes from standard English, where "bi-monthly" can mean twice a month or every two months.
When comparing bi-monthly vs bi-weekly in payroll, the key distinction is timing. Bi-weekly pay always lands on the same day of the week. Bi-monthly pay always falls on the same dates of the month. So, bimonthly vs biweekly or biweekly vs bimonthly are the most common payroll comparisons.
What about bimonthly vs semimonthly? In payroll, these terms are interchangeable. Both mean two paychecks per month. The bi-monthly label only gets confusing outside of payroll, where it could mean every other month.
For tax purposes, neither schedule changes your total IRS bill. One of the best practices is to check your IRS tax withholding tables for the correct per-paycheck amount based on payroll frequency. The bi-weekly vs bi-monthly difference is simply a matter of weekday vs date consistency. Searching bi-monthly vs bi-weekly leads to 24 vs 26 paychecks. The same applies when comparing semi-monthly vs bi-monthly.
How To Calculate Semi-Monthly Pay
Now that the semi-monthly meaning is clear, let's look at the math.
Divide your gross yearly salary by 24. You can also use a paycheck calculator for quick estimates.
Formula: Semi monthly pay = Annual salary / 24
Example: $60,000 / 24 = $2,500 per check (before taxes)
For hourly workers, each pay period covers about 86.67 hours (2,080 yearly hours / 24). Multiply your hourly rate by 86.67 to get your gross semi-monthly pay. For a full breakdown, see our guide on how to calculate your hourly, weekly, and monthly income.
Your net pay will be lower after payroll processing deducts federal and state taxes, health insurance premiums, and 401(k) contributions from each paycheck. Each semi-monthly pay period covers roughly 86.67 work hours for full-time staff.
Pros and Cons of Semi-Monthly Pay
For employees:
-
Larger paychecks than biweekly (fewer pay periods means more per check)
-
Set pay dates that match monthly bills and budgeting
-
Benefit deductions split evenly across two monthly checks
Drawbacks for employees:
-
No "bonus" paycheck months (biweekly gives you two extra checks per year)
-
Longer wait between paychecks if you're used to weekly or biweekly pay
-
No on-demand pay option in most semi-monthly setups
For employers:
-
Fewer payroll runs reduce administrative burden and payroll costs
-
Easier cash flow management with consistent monthly expenses
-
Benefit deductions align cleanly with monthly billing cycles
Drawbacks for employers:
-
Pay dates falling on weekends require advance processing
-
Overtime pay math is harder for hourly staff
Does the Semi-Monthly Meaning Affect Your Taxes?
No. Semi-monthly pay does not change your total tax bill. Taxes are based on yearly income, not how often you get paid. Your total tax withholding stays the same whether you receive 24 semi-monthly paychecks or 26 biweekly ones. Only per-check amounts differ.
Your employer's payroll software adjusts each paycheck based on the pay periods per year. Your salary, filing status, and W-4 choices set your total tax bill. People debating biweekly vs semi-monthly pay schedules should know taxes are the same either way. Learn more about FIT taxable wages on your paycheck.
How To Choose the Right Pay Schedule
Choosing between semi-monthly and biweekly depends on a few key factors. The semi-monthly vs bi-weekly choice affects payroll operations, employee satisfaction, and cash flow:
-
State Labor Laws: Some states restrict semi-monthly pay for hourly workers. Check Department of Labor regulations for your state's rules.
-
Workforce Type: Salaried employees fit well with semi-monthly pay. Hourly employees often prefer biweekly for simpler overtime calculations.
-
Business Needs: Think about your company's cash flow and payroll software setup. Is it better to get paid weekly or biweekly? That depends on your industry and what your team prefers.
Semi-weekly vs bi-weekly is another term people confuse. Semi-weekly means twice per week, which is rare. Biweekly vs semiweekly pay schedules serve very different employee needs.
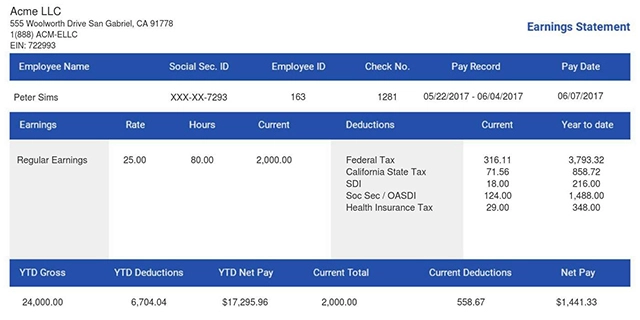
How the Semi-Monthly Meaning Shows up on Your Pay Stub
Your pay stub on a semi-monthly schedule shows gross pay as 1/24 of your yearly salary. Each stub lists taxes, insurance, and retirement for that pay period. Reading pay stub deduction codes helps you verify each line item.
Check the YTD section. After 12 pay periods (mid-year), your YTD gross should equal half your yearly salary. If it doesn't, flag it with payroll.
Need pay records for a loan or rental? Our pay stub templates make it easy to create clean records.
You Might Also Like
To Sum It Up
Understanding the semi-monthly meaning can help with financial planning and smarter budgeting. The core takeaway is that semi-monthly means twice a month on fixed dates for 24 annual paychecks. Biweekly means every two weeks for 26 paychecks. Your annual salary and taxes stay the same either way.
Need professional pay documentation? A reliable paystub generator makes it easy to create accurate pay stubs in minutes.