What is a Non Exempt Employee? - The Full Guide
A non-exempt employee is an individual that does not have to be paid overtime for working more than 40 hours in one week, or any other type of work week.
The only people who are exempt from the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) are those employees listed as exempt in 29 CFR Part 541.
These exemptions include jobs such as attorneys, accountants, engineers, architects, dentists, etc.
If you are unsure if your job is exempt, contact your human resources department and ask them what they think. Still, let's take a look at what a non-exempt employee is in more detail.
- What is the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)?
- Who Is An “Employee” Under the Fair Labor Standards Act?
- What Does the Word “Exempt” Actually Mean?
- What Does the Term “Non-Exempt” Mean Then?
- How Do I Know Whether, or Not, I Am Covered By the Fair Labor Standards Act?
- Are There Any Other Types of Employees Who Must Be Paid Overtime?
- What is the FLSA Rule on Overtime?
- Can My Employer Reduce My Pay Below Minimum Wage?
- Can My Employer Require Me to Work More Than 40 Hours Per Week?
- Final Thoughts

What is the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA)?
In 1938, Congress passed the Fair Labor Standards Act which was designed to protect workers from being exploited by their employers. The FLSA requires all employers to pay their employees a minimum wage and provides time-and-a-half compensation for all hours worked over forty per week.
It also prohibits employers from paying less than the federal minimum wage to any worker. It also requires employers to provide a safe workplace free of hazards like toxic chemicals.
The FLSA also establishes maximum workweeks and maximum daily work hours. For example, it says that no employer can require anyone to work more than 48 hours per week or 52 weeks per year.
The FLSA also sets rules about how much money must be paid to certain categories of workers including:
-
Overtime
-
Child Labor Laws
-
Record Keeping Requirements
-
Worker Protection Programs
-
Workers' Compensation
Who Is An “Employee” Under the Fair Labor Standards Act?
An employee is defined under the FLSA as someone who works for another person or company and receives wages or salary. This includes independent contractors, temporary help agencies, part-time employees, interns, and volunteers.
An employee may be considered a contractor if the employer controls the means and manner of performing the work. If the employer has control over the worker, then the worker is not an employee.
For example, if a construction company hires a subcontractor to build a house, then the construction company would be considered the employer.
However, if the same construction company hired a plumber to install pipes, then the plumber would be considered an employee because he/she did not have control over his/her own work.
So, if you do not consider yourself an employee, but still want to know whether, or not, you are covered by the FLSA, you need to determine if you meet the definition of an employee.
Also read: 8 Best Ideas for Home Office Organization
What Does the Word “Exempt” Actually Mean?
When referring to employees, the word “exempt” actually refers to two different things.
First, there is the exemption from the FLSA itself. That is, people who are exempt from having to comply with the FLSA.
Second, there is the exemption for specific types of jobs. These exemptions are found in Section 13(a)(1) of the FLSA. They include:
-
Attorneys
-
Accountants
-
Architects
-
Doctors
-
Dentists
-
Engineers, etc.
What Does the Term “Non-Exempt” Mean Then?
If you are not exempt, then you are considered a non-exempt employee. A non-exempt employee is one who does not fall into any of these categories and therefore must receive overtime pay.
Also read: 7 Thoughtful Farewell Gifts for Coworkers

How Do I Know Whether, or Not, I Am Covered By the Fair Labor Standards Act?
To figure out whether, or not, you are protected by the FLSA, here's what you should look at:
-
Are your wages below $455 per month (the current federal minimum wage)?
-
Have you been employed for more than 240 hours in a calendar year?
-
Do you perform duties that are directly related to your job?
-
Do you spend most of your time working within your place of work?
These questions will tell you whether, or not, you qualify as an employee under the FLSA. You should consult an attorney if you have any doubts about this.
Also read: 8 Great Virtual Retirement Party Ideas
Are There Any Other Types of Employees Who Must Be Paid Overtime?
Yes! In addition to all regular employees, there are other groups of individuals who must be paid overtime. These include:
-
Domestic Workers
-
Transportation Workers
-
Fishing Vessel Crew Members
-
Seamen
-
Firefighters, etc.
What is the FLSA Rule on Overtime?
The rule regarding overtime is simple: All employees must be compensated for their time worked beyond 40 hours in a week. For example, if an employee works 50 hours during a seven-day period, they must be paid for 7 additional hours.
However, employers can choose to pay their workers less than the required amount of overtime compensation. This is called “substituting overtime pay.” The law allows employers to substitute overtime pay for some of the regular pay given to their employees.
However, substituting overtime pay cannot be used to reduce the amount of regular pay owed to employees. If it were allowed, the law would be circumvented.
For example, if a worker was paid $10 per hour for a 40-hour workweek, the employer could only pay him $8 per hour for the first 8 hours of the workweek. He would get no extra money for the last 32 hours.
This means that the employer has to pay the worker $2 extra per hour for those 32 hours. However, the employer may not subtract that amount from his total payment.
This is because the employer is still paying the worker $10 per hour for the full 40 hours he works each week.
Can My Employer Reduce My Pay Below Minimum Wage?
No. Your employer cannot pay you less than the minimum wage. If he pays you less than the minimum, he is violating the law.
Also read: Learning Programs For Startup Employees During Pandemic
Can My Employer Require Me to Work More Than 40 Hours Per Week?
Yes. An employer can require his employees to work longer than 40 hours per week. The law states that the employer must compensate the employee for all hours worked over 40.
If you want to know how much you are entitled to receive, check with a lawyer.
Also read: 10 Best Work-Life Balance Jobs in the USA

Final Thoughts
A non-exempt employee is someone who earns less than $455 per month and works more than 240 hours in one calendar year. They also need to do certain things to be considered exempt.
You can find out whether, or not, you're covered by the FLSA by asking yourself these questions:
-
Have you been employed for more than 240 hours in a calendar year?
-
Does your job involve performing duties that are directly related to your job?
-
Do most of your duties take place at your workplace?
If you're unsure, you can always ask HR to clear up any confusion.
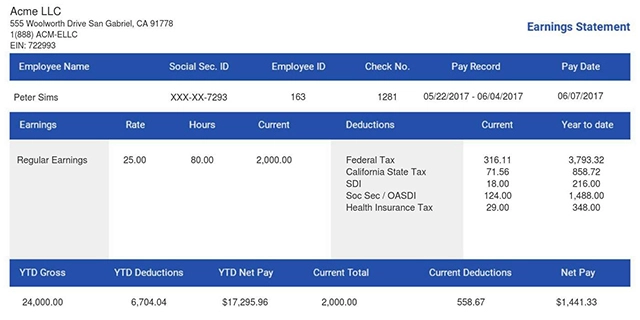
Using our pay stub generator you can ensure that you are receiving quality pay stubs on a regular basis.